Extrapolation is a method of predicting/estimating new data value(s) beyond a discrete set of known data values. Extrapolation can be similar to the method of interpolation, which predicts new data values within known data values.
NOTE: data values that are the result of extrapolation from statistical data are often less valid then those that are the result of interpolation.
Given: The sequence of values (representing a pattern of numbers) below.
3, 5, 7, 9, ... .
If we needed to know the next number in the sequence, we would need to extrapolate, since we are looking for a value beyond the known data values.
It appears that two is added to any member of the sequence to get the next member of the sequence. If two is added to the last number (nine), a result of eleven occurs. Eleven is a value extrapolated from known values of the sequence of numbers.
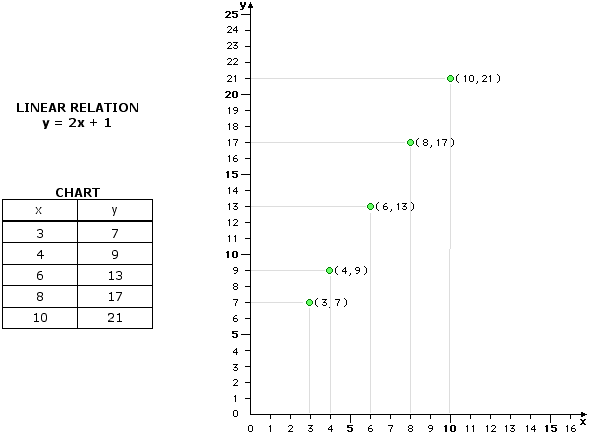
Given: A linear relation with a corresponding chart of values and the corresponding graph below.
We would have to extrapolate to find y-values that correspond to x-values smaller than 3 and we would have to extrapolate to find y-values that correspond to x-values larger than 10.
Given an x-value of 12, the corresponding y-value could be extrapolated as 25.
y = 2(12) + 1
y = 24 + 1
y = 25