Additional Sample Questions
These questions are provided as sample multiple-choice questions that meet
the criteria and address learner outcomes in the 2007 program of studies
for the Social Studies 20-1 and 20-2 sequences.
1. Use the newspaper headlines to answer the following
question.

On which issue do all four newspaper headlines most
directly focus?
- Should the victors in a war form a military alliance?
- Should the victors in a war dictate the terms of peace?*
- Should an agency of collective security grant certain members special
privileges?
- Should an agency of collective security interfere in the domestic affairs
of its members?
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-1 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
evaluate ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple and varied sources of information
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-2 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
analyze ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple sources of information |
| S.1.9 |
identify main ideas underlying a position or issue
|
2. Use the illustration to answer the following question.
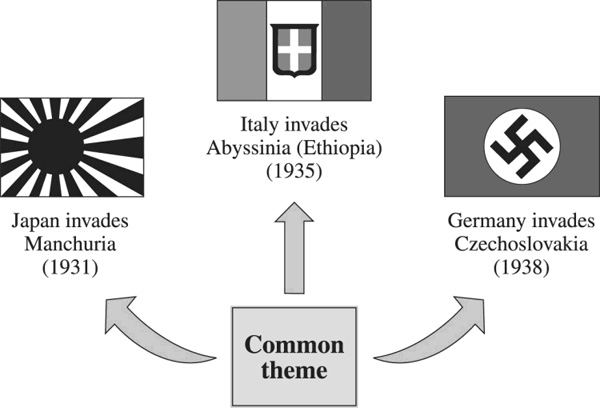
The "common theme" of this diagram is the League of Nations':
- Resistance to foreign diplomatic negotiations
- Success in resolving international conflict
- Inability to stop imperialist aggression*
- Encouragement of self-determination
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-1 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
evaluate ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple and varied sources of information
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-2 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
analyze ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple sources of information |
| S.1.9 |
identify main ideas underlying a position or issue
|
3.
During the period between the First World War
and the Second World War, American foreign policy was primarily based on
ideas related to:
- Militarism
- Imperialism
- Isolationism*
- Internationalism
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
4.
The official purpose of the conferences held near
Paris immediately following the First World War was to:
- Provide a forum for the meeting of the League of Nations
- Form a new balance of power along ideological lines
- Decide how to prevent the spread of communism
- Draw up provisions for a lasting peace in Europe*
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
5.
Which of the following statements best summarizes
the intent of the Treaty of Versailles?
- The treaty must punish all the losers of the First World War.*
- The treaty must be signed and supported by all victors of the First World
War.
- All nations that participated in the First World War must be treated
fairly by the treaty.
- The input of all nations that participated in the First World War must
be taken into account by the treaty.
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
6.
Initially, the United States hesitated to enter
the Second World War because the American government was pursuing a foreign
policy of:
- Isolationism*
- Appeasement
- Confrontation
- Interventionism
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
7.
The Treaty of Versailles was created primarily
to:
- Establish a military alliance of non-communist European nations
- Outline the organizational structure for the League of Nations
- Ensure open and fair diplomacy between nations of the world
- Detail the terms of peace settlement with Germany*
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
8.
The American policy of isolationism after the
First World War clashed most directly with the ideas and
principles of:
- Nationalism
- Humanitarianism
- Self-Determination
- Collective Security*
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.5 |
analyze how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.6 |
examine how the pursuit of national interest shapes foreign policy
(First World War peace settlements, the interwar period) (PADM, TCC,
ER, LPP)
|
9. Use the following events to answer the question.

The progression of events shown above suggests that Nazi Germany confidently
pursued and applied foreign policies of:
- Imperialism and Militarism*
- Regionalism and Imperialism
- Nationalism and Isolationism
- Militarism and Internationalism
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.7 |
analyze nationalism and ultranationalism during times of conflict (causes
of the First and Second World Wars, examples of nationalism and ultranationalism
from the First and Second World Wars, ultranationalism in Japan, internments
in Canada, conscription crises) (PADM, TCC, GC, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-1 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
evaluate ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple and varied sources of information |
| S.1.6 |
synthesize information from contemporary and historical issues to develop
an informed position |
| S.2.6 |
identify reasons underlying similarities and differences among historical
narratives
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.8 |
analyze nationalism and ultranationalism during times of conflict
(causes of the First and Second World Wars, examples of nationalism and
ultranationalism from the First and Second World Wars, internments in
Canada, conscription crises) (PADM, TCC, GC, LPP)
|
Skills and Processes 20-2 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
analyze ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple sources of information |
| S.1.7 |
identify seemingly unrelated ideas to explain a concept or event |
| S.2.7 |
develop reasoned arguments supported by historical and contemporary
evidence |
10.
Territorial expansion to provide living space
for a "master race" was used to justify actions taken by:
- France immediately after the First World War
- Germany in the late 1930s*
- China prior to the Second World War
- The Soviet Union in the late 1940s
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.7 |
analyze nationalism and ultranationalism during times of conflict (causes
of the First and Second World Wars, examples of nationalism and ultranationalism
from the First and Second World Wars, ultranationalism in Japan, internments
in Canada, conscription crises) (PADM, TCC, GC, LPP)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.8 |
analyze nationalism and ultranationalism during times of conflict (causes
of the First and Second World Wars, examples of nationalism and ultranationalism
from the First and Second World Wars, internments in Canada, conscription
crises) (PADM, TCC, GC, LPP)
|
11.
The "Final Solution" was an attempt
by Germany to:
- Invade and conquer the Soviet Union
- Destroy civilian morale by bombing cities
- Invade and occupy France and the low countries
- Annihilate European Jews and other ethnic groups*
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 2.8 |
analyze ultranationalism as a cause of genocide (the Holocaust, 1932–1933
famine in Ukraine, contemporary examples) (TCC, PADM, GC)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 2.9 |
examine ultranationalism as a cause of genocide (the Holocaust, the
1932–1933 famine in Ukraine, contemporary examples) (TCC, PADM,
GC)
|
12.
At the Paris Peace Conference of 1919, President
Woodrow Wilson supported the principle of self-determination in the hope
that:
- National groups in Europe would have the right to form independent nations*
- Germany would be blamed for the destruction caused during the First World
War
- A military alliance between France, Great Britain and the United States
would be created
- European nations would accept the American sphere of influence established
in Latin America
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 3.4 |
analyze the motives of nation and state involvement or noninvolvement
in international affairs (economic stability, self-determination, peace,
security, humanitarianism) (GC, TCC, PADM)
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 3.4 |
examine the motives of nation and state involvement or noninvolvement
in international affairs (economic stability, self-determination, peace,
security, humanitarianism) (GC, LPP, TCC)
|
13. Use the following information to answer the question.
The League of Nations failed primarily as a result of two reasons: one,
the lack of universality in its membership; and two, the unwillingness of
the League to consider military action. This second reason was understandable
considering the slaughter of the Second World War; however, the unwillingness
to use military action proved to be a critical error. Following the Second
World War, the creators of the Charter of the United Nations showed evidence
that they had learned from the past experiences of the League of Nations.
To prevent a similar situation such as the second reason, the United Nations
has claimed the authority to:
- Allow Security Council members to veto power
- Impose economic sanctions to enforce collective security
- Intervene with force in disputes that are caused by aggression*
- Violate national sovereignty during times of international crisis
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcome:
| 3.7 |
evaluate the extent to which selected organizations promote internationalism
(United Nations, World Council of Indigenous Peoples, European Union,
L'Organisation internationale de le Francophonie, Arctic Council, contemporary
examples) (GC, PADM, ER)
|
Skills and Processes 20-1 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
evaluate ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.2.2 |
analyze connections among patterns of historical change by identifying
cause and effect relationships |
| S.2.4 |
evaluate the impact of significant historical periods and patterns
of change on the contemporary world
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcome:
| 3.7 |
analyze the extent to which selected organizations promote internationalism
(United Nations, World Council of Indigenous Peoples, European Union,
l'Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, Arctic Council) (GC,
PADM, ER)
|
Skills and Processes 20-2 outcomes:
| S.1.1 |
analyze ideas and information from multiple sources |
| S.1.9 |
identify main ideas underlying a position or issue |
| S.2.2 |
analyze connections among patterns of historical change by identifying
cause and effect relationships |
| S.2.4 |
identify and describe the impact of significant historical periods
and patterns of change on society today
|
14. Use the information to answer the following question.
| 1987 |
After taking over Serbia's ruling League of Communists, Milosevic became
a hero to the Serbs. |
| 1990 |
Following the collapse of communist rule, Milosevic is freely re-elected
president of Serbia. |
| 1991 |
Yugoslavia breaks up as Slovenia and Croatia declare independence.
Fighting erupts in Croatia and Bosnia. |
| 1992 |
Serbia and Montenegro form a new Yugoslav federation. The United Nations
imposes economic sanctions on Yugoslavia for inciting war in Croatia
and Bosnia, where thousands of atrocities are committed. |
| 1995 |
After intense negotiations, spearheaded by the United States, a peace
accord regarding Bosnia is signed in Dayton, Ohio. |
| 1998 |
Tensions rise in Kosovo amid reports of Serbian atrocities committed
against local Muslims of Albanian ancestry. |
| 1999 |
NATO starts its air war against Serbian forces. In June, Milosevic
concedes defeat and withdraws his forces from Kosovo. |
| 2000 |
Running for re-election, Milosevic faces a surprisingly strong challenge
from Vojislav Kostunica, who wins in the first round of balloting. Massive
protests finally persuade Milosevic to resign. |
Which of the following titles is most appropriate for the information provided?
- "The Rise and Fall and Slobodan Milosevic"*
- "The Western States Legitimize the Milosevic Regime"
- "The Consequences of United Nations Intervention in Yugoslavia"
- "The Failure of Collective Security to Prevent the Rise of a Dictator"
Knowledge and Understanding 20-1 outcomes:
| 3.8 |
analyze impacts of the pursuit of internationalism in addressing contemporary
global issues (conflict, poverty, debt, disease, environment, human rights)
(GC, PADM, ER) |
| 3.9 |
evaluate the extent to which nationalism must be sacrificed in the
interest of internationalism (GC, PADM, ER)
|
Skills and Processes 20-1 outcomes:
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple and varied sources of information |
| S.1.4 |
predict likely outcomes based on factual information |
| S.2.2 |
analyze connections among patterns of historical change by identifying
cause and effect relationships
|
Knowledge and Understanding 20-2 outcomes:
| 3.8 |
examine impacts of the pursuit of internationalism in addressing contemporary
global issues (conflict, poverty, debt, disease, environment, human rights)
(GC, PADM, ER) relationships among multiple and varied sources of information |
| 3.9 |
evaluate the extent to which nationalism must be sacrificed in the
interest of internationalism (GC, PADM, ER)
|
Skills and Processes 20-2 outcomes:
| S.1.2 |
determine relationships among multiple sources of information |
| S.1.4 |
suggest likely outcomes based on factual information |
| S.2.2 |
analyze connections among patterns of historical change by identifying
cause and effect relationships |
|






